Endurance athletes require optimal nutrition to fuel their body during intense training and competitions. The demands of such activities put significant strain on the muscles and cardiovascular system, making it crucial for athletes to consume the right balance of macronutrients and micronutrients to enhance performance and aid in recovery. In this article, we will explore the key components of a well-rounded endurance athlete’s diet.
The Importance of Carbohydrates
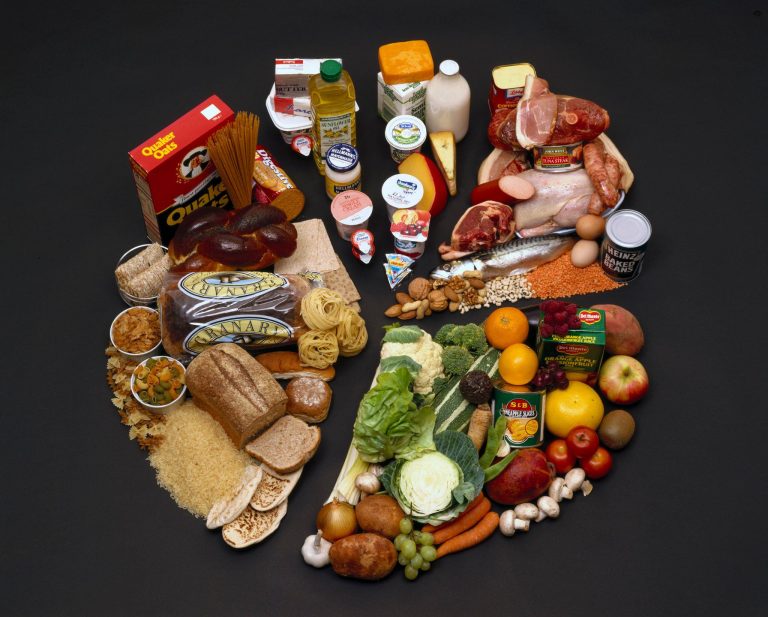
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for endurance athletes. Consuming adequate amounts of carbohydrates before, during, and after exercise helps maintain blood glucose levels and replenishes glycogen stores in the muscles. Complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables provide a steady release of energy, while simple carbohydrates like sports drinks and gels offer quick energy during exercise.
Protein for Muscle Repair
Protein plays a crucial role in repairing and rebuilding damaged muscle tissue. Endurance athletes require slightly more protein than the average person to support muscle recovery and growth. Good sources of protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, and plant-based sources such as beans, lentils, tofu, and tempeh. It is important for athletes to consume protein throughout the day, including before and after exercise, to optimize muscle repair.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals play a vital role in overall health and performance. Endurance athletes should prioritize consuming a wide variety of fruits and vegetables to ensure adequate intake of vitamins and minerals. Vitamin C, E, and A are particularly important for their antioxidant properties, which help protect the body from oxidative stress induced by exercise. Iron, calcium, and magnesium are also crucial minerals for endurance athletes to support oxygen transport, bone health, and muscle function.
Hydration: The Key to Success
Proper hydration is paramount for endurance athletes as even mild dehydration can impair performance. Athletes should aim to drink enough fluids throughout the day, not just during exercise. Water is the best choice for hydration, but for intense workouts lasting longer than an hour, sports drinks containing electrolytes can help replenish sodium and other minerals lost through sweat.
Timing and Frequency of Meals
The timing and frequency of meals is crucial for endurance athletes to optimize performance and recovery. Consuming a balanced meal containing carbohydrates, protein, and fats 2-3 hours before exercise helps top up energy stores and prevent hunger during the workout. During long training sessions or competitions lasting more than an hour, consuming small snacks or sports drinks every 20-30 minutes can help maintain energy levels. Lastly, post-exercise, it is important to consume a combination of carbohydrates and protein within 30 minutes to facilitate muscle repair and replenish glycogen stores.
Supplements for Endurance Athletes
While a well-rounded diet can provide the necessary nutrients, some endurance athletes may benefit from certain supplements. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before introducing any supplements. Common supplements include sports drinks, energy gels, electrolyte tablets, and protein shakes. These supplements can be useful during long-duration workouts or competitions when it may be difficult to consume whole foods.
Tailoring Nutrition to Specific Sports
Each endurance sport comes with its unique demands, and therefore nutrition requirements may vary. For example, a cyclist may benefit from consuming more carbohydrates, while a long-distance runner may require additional electrolytes. It is essential for athletes to work with a sports nutritionist to tailor their diet to their specific sport and individual needs.
Conclusion
Nutrition plays a critical role in the performance and recovery of endurance athletes. A diet rich in carbohydrates, protein, vitamins, and minerals, along with proper hydration, helps optimize training and competition outcomes. Understanding the importance of timing meals and tailoring nutrition to specific sports can enhance an athlete’s overall performance, endurance, and well-being.