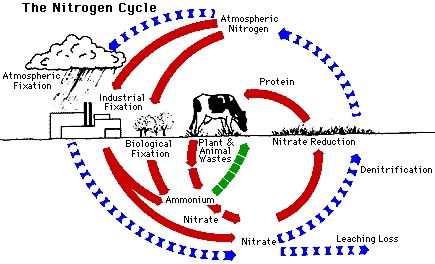
In recent years, there has been an increasing focus on sustainable farming practices as the negative impacts of conventional farming on the environment and human health have become more apparent. Sustainable farming aims to preserve the natural resources, minimize waste, and promote biodiversity while ensuring the production of high-quality, nutrient-rich food. Here are some key sustainable farming practices that are gaining popularity:
1. Organic Farming
Organic farming involves the use of natural fertilizers and pest control methods, avoiding synthetic chemicals, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and antibiotics. It focuses on enhancing soil health through practices like crop rotation, composting, and cover cropping. Organic farming reduces soil erosion, improves water quality, and supports biodiversity as it incorporates ecological principles into agricultural systems.
2. Agroforestry
Agroforestry is a practice that combines agriculture with the cultivation of trees and shrubs. It provides multiple benefits such as reducing soil erosion, improving water retention, and sequestering carbon dioxide. By integrating trees into farming systems, agroforestry enhances biodiversity, provides shade and wind protection, and creates habitats for wildlife. It also enables farmers to diversify their income by selling timber, fruits, nuts, or medicinal plants alongside traditional crops.
3. Conservation Tillage
Conservation tillage is a set of soil management practices that minimize soil disturbance. It involves reducing or eliminating plowing and leaving the crop residues on the field as a protective covering. By leaving the soil undisturbed, conservation tillage prevents erosion, improves water infiltration, and preserves soil structure. This practice also reduces fuel consumption, machinery costs, and labor requirements, making it economically beneficial for farmers.
4. Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture utilizes technology and data analysis to optimize farming operations. It involves using GPS, sensors, and remote sensing tools to monitor crop health, soil moisture, and nutrient levels. By precisely applying fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation, precision agriculture minimizes waste, reduces chemical runoff into water bodies, and ensures efficient resource utilization. This approach enables farmers to make informed decisions, increase yields, and minimize the environmental impact of farming.
5. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management is a sustainable approach to pest control that emphasizes the use of natural predators, biological controls, and cultural practices to manage pests. By reducing the reliance on chemical pesticides, IPM minimizes potential harm to the environment and human health. It involves regular monitoring, pest identification, and the implementation of strategies such as crop rotation, habitat manipulation, and the use of pheromone traps. IPM aims to maintain pest populations at tolerable levels while minimizing the impact on beneficial insects and biodiversity.
6. Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation is an efficient water management technique that delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing water loss due to evaporation and surface runoff. This method saves water and reduces energy consumption compared to traditional flood or overhead irrigation systems. By providing water precisely where it is needed, drip irrigation improves crop health, minimizes weed growth, and optimizes nutrient uptake. It is particularly useful in arid and drought-prone regions where water resources are limited.
7. Crop Rotation
Crop rotation involves the sequential planting of different crops in the same field over multiple seasons. It helps to disrupt pest and disease cycles, increase soil fertility, and reduce the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. Different crops have varying nutrient requirements, root structures, and natural defense mechanisms. By rotating crops, farmers can improve soil health, break pest cycles, and promote biodiversity by providing diverse habitats for beneficial organisms.
8. Cover Cropping
Cover cropping involves planting specific crops, often legumes or grasses, to cover the soil in between main crop seasons. It protects the soil from erosion, suppresses weed growth, enhances soil fertility, and increases organic matter. Cover crops help to build healthy soil by fixing nitrogen, balancing soil pH, and improving soil structure. They also provide habitats for pollinators and beneficial insects, contributing to overall ecosystem health.
Conclusion
Sustainable farming practices play a crucial role in reducing the environmental impact of agriculture while ensuring the long-term productivity of our food systems. By adopting organic farming, agroforestry, conservation tillage, precision agriculture, integrated pest management, drip irrigation, crop rotation, and cover cropping, farmers can promote resource efficiency, protect biodiversity, and produce healthier food. It is essential to encourage the widespread adoption of these practices to achieve a more sustainable and resilient agricultural system for future generations.