Food security and access are critical concerns in today’s world. With a growing global population and various socio-economic issues, ensuring that everyone has access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food has become a significant challenge. In this article, we will explore the concept of food security and discuss the importance of addressing food access for a sustainable future.
Defining Food Security
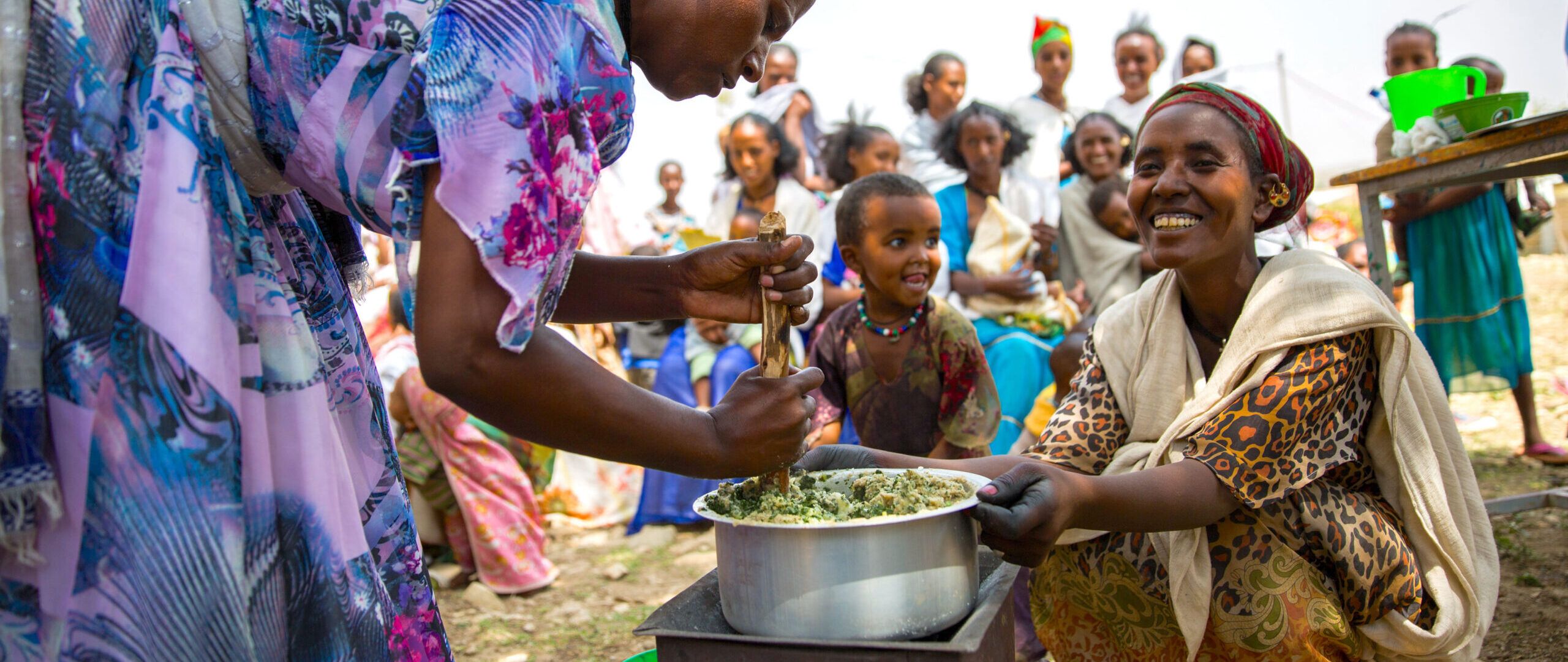
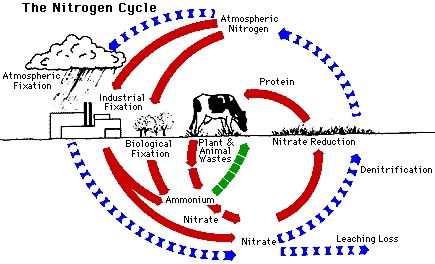
Food security refers to the state in which all individuals have physical, social, and economic access to adequate, safe, and nutritious food that meets their dietary needs and preferences for an active and healthy life. It encompasses both the availability and accessibility of food. Achieving food security requires a multifaceted and holistic approach that considers various factors, including agricultural production, distribution, purchasing power, and nutritional value.
The Importance of Food Security
Food security is vital for the well-being and development of individuals, communities, and nations. When people have access to sufficient and nutritious food, they are more likely to lead healthy and productive lives. It also helps to alleviate poverty, reduce malnutrition, and improve overall public health. Furthermore, food security plays a crucial role in creating stability and peace within societies by preventing conflicts arising from competition over limited resources.
Challenges in Achieving Food Security
Despite significant progress in agricultural practices and technology, numerous challenges hinder the attainment of global food security. These challenges include:
Climate Change: The increasing occurrence of extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, negatively affects agricultural productivity and disrupts food production.
Poverty: Poverty and income inequality limit people’s purchasing power, preventing them from accessing sufficient and nutritious food.
Conflict and Instability: Areas affected by conflict and political instability face significant challenges in producing, distributing, and accessing food, leading to food shortages and malnutrition.
Limited Agricultural Resources: Limited availability of arable land, water scarcity, and depletion of natural resources pose obstacles to agricultural production.
Addressing Food Access
Improving food access is a crucial aspect of achieving food security. Here are some approaches to consider:
Supporting Small-scale Farmers
Small-scale farmers, particularly in developing countries, play a significant role in food production. Supporting them through access to resources, training, and fair markets can enhance their productivity and livelihoods.
Investing in Agricultural Infrastructure
Investing in agricultural infrastructure, such as irrigation systems, transportation networks, and storage facilities, can improve efficiency in food production and distribution, reducing post-harvest losses and ensuring food reaches consumers in a timely manner.
Promoting Sustainable Agricultural Practices
Encouraging sustainable farming practices, such as organic farming and agroforestry, can help protect the environment, preserve biodiversity, and improve long-term agricultural productivity.
Enhancing Social Safety Nets
Establishing social safety nets, such as cash transfer programs and food assistance initiatives, can provide vulnerable populations with the means to access nutritious food in times of economic or environmental crises.
Strengthening Global Cooperation
Enhancing international partnerships and cooperation is essential for addressing food security challenges on a global scale. Collaboration between governments, non-governmental organizations, and international institutions can foster knowledge sharing, policy development, and resource mobilization.
Conclusion
Food security and access are fundamental for the well-being, health, and development of individuals and societies. Tackling the challenges of food security requires a comprehensive and collaborative approach, focusing on addressing the underlying causes of food insecurity and investing in sustainable agriculture and infrastructure. By ensuring that everyone has access to sufficient and nutritious food, we can create a more equitable and prosperous future for all.