In recent years, there has been a growing concern about the impact of climate change on various aspects of our lives, including our nutrition. Climate change affects the availability, quality, and cost of food, ultimately impacting our diets and nutritional well-being. In this article, we will explore the connection between nutrition and climate change, and discuss the steps we can take to ensure a sustainable and healthy diet.
Impact on Food Production
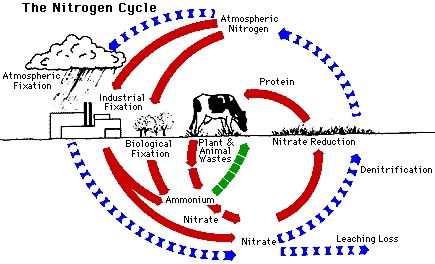
Climate change leads to changes in weather patterns, including extreme events such as droughts, floods, and heatwaves. These extreme events can have a detrimental effect on agricultural productivity and livestock production. Droughts, for example, can lead to reduced water availability for irrigation, resulting in decreased crop yields and lower nutritional value in the harvested produce. Floods, on the other hand, can destroy entire crops, leading to food shortages and increased food prices.
Rising temperatures also have negative implications for food production. Certain crops, such as wheat and maize, are particularly sensitive to high temperatures, leading to decreased yields. Additionally, increasing temperatures can also affect the nutritional composition of crops, reducing their content of important vitamins and minerals.
Loss of Biodiversity
Climate change also contributes to the loss of biodiversity, which has a direct impact on our nutrition. The loss of biodiversity affects pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control. Bees, for example, play a crucial role in pollinating many crops, and their decline can result in reduced yields of fruits and vegetables. Furthermore, the loss of diverse ecosystems makes agricultural systems more vulnerable to pests, increasing the use of pesticides, which can have adverse effects on human health.
Changes in Food Availability and Affordability
Climate change can disrupt food supply chains, affecting the availability and affordability of certain foods. Extreme weather events and changing environmental conditions can disrupt transportation systems, leading to delays and spoilage of food products. These disruptions can have a disproportionate impact on vulnerable communities who already struggle with food insecurity.
Furthermore, climate change can also affect the affordability of food. As the production costs increase due to water scarcity, extreme weather events, and higher energy prices, the prices of food items are likely to rise. This can make nutritious foods less accessible to low-income populations, leading to an increase in malnutrition and related health issues.
Adapting to Climate Change: Sustainable Diets
To mitigate the adverse effects of climate change on nutrition, it is crucial to promote sustainable diets. A sustainable diet is one that is nutritious, environmentally friendly, and accessible to all. It emphasizes plant-based foods, reduces food waste, and promotes locally sourced and seasonal ingredients.
Increasing the consumption of plant-based foods, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, is not only beneficial for our health but also has a lower carbon footprint compared to animal-based products. Reducing the consumption of meat and dairy products can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and alleviate pressure on natural resources.
Minimizing food waste is another important aspect of sustainable diets. Around one-third of all food produced globally is wasted, contributing to the emissions of greenhouse gases. By practicing mindful shopping, proper storage, and creative use of leftovers, we can significantly reduce food waste and its climate impact.
Furthermore, supporting local agriculture and consuming seasonal produce can also contribute to a more sustainable diet. Locally sourced foods require less transport, thus reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with long-distance food transportation. Additionally, consuming seasonal foods not only supports local farmers but also ensures a variety of nutrients in our diet.
Conclusion
Nutrition and climate change are closely intertwined. The impact of climate change on food production, loss of biodiversity, food availability, and affordability directly affects our diets and nutritional well-being. To alleviate these problems, adopting sustainable diets that are plant-based, minimize food waste, and support local agriculture is crucial. By making conscious and environmentally friendly choices, we can contribute to a healthier future for both ourselves and the planet.