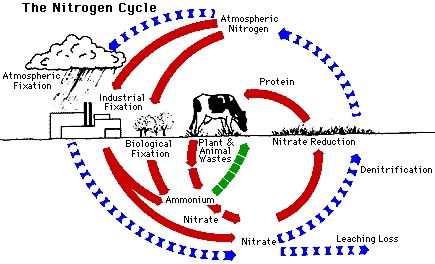
Food waste is a major global issue that not only affects our economy and environment but also exacerbates hunger and poverty. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, approximately one-third of the food produced in the world for human consumption every year is wasted. This amounts to about 1.3 billion tons of food waste, and the consequences are far-reaching.
Environmental Consequences
One of the most significant impacts of food waste is its contribution to environmental degradation. The resources that go into food production, including water, energy, and land, are wasted when food is thrown away. This leads to a squandering of precious natural resources and exacerbates issues such as water scarcity and deforestation.
Furthermore, when food waste ends up in landfills, it produces methane gas as it decomposes. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change, with a global warming potential 25 times greater than carbon dioxide. The accumulation of food waste in landfills significantly adds to the overall greenhouse gas emissions and exacerbates the problem of climate change.
Economic Consequences
Food waste also has significant economic implications. The costs associated with food production, transportation, and storage are wasted when food is discarded. In both developed and developing countries, food waste accounts for a substantial loss of money and resources. This loss has a direct impact on food prices, making it more difficult for vulnerable populations to access healthy and affordable food.
Moreover, the disposal of food waste also incurs additional expenses. Local municipalities and governments have to bear the costs of collection, transportation, and disposal of the waste, which could otherwise have been diverted to more productive uses.
Social Consequences
The impact of food waste extends beyond the environmental and economic spheres to affect society as a whole. Wasted food represents a missed opportunity to alleviate hunger and poverty. It is estimated that if just a quarter of the food wasted globally could be saved, it would be enough to feed 870 million hungry people.
Food waste also exacerbates inequality by further marginalizing vulnerable populations. When nutritious food is thrown away while millions suffer from malnutrition and hunger, it highlights the inequities present in our food system. Addressing food waste is not only a matter of environmental and economic sustainability but also a matter of social justice.
Solutions to Combat Food Waste
Addressing the issue of food waste requires a comprehensive and multi-faceted approach. Here are some strategies that can help combat this global problem:
1. Consumer Awareness and Education
Improving public awareness and education about the impacts of food waste is crucial in encouraging behavioral change. Educating individuals about proper food storage, portion planning, and utilizing leftovers can significantly reduce household food waste.
2. Improved Food Storage and Distribution
Investing in better storage infrastructure and technologies throughout the food supply chain can prevent spoilage and extend the shelf life of perishable items. Additionally, improving distribution networks can reduce food losses during transportation and ensure that excess food is efficiently redistributed to those in need.
3. Collaboration and Partnerships
Creating partnerships between food producers, retailers, and charitable organizations can facilitate the donation of surplus food to food banks and community organizations. This collaboration can help redirect edible food from being wasted to feeding hungry individuals.
4. Policy and Regulation
Governments can play a crucial role in addressing food waste by implementing policies and regulations that discourage waste. This can include incentivizing food recovery and redistribution, implementing landfill diversion targets, and promoting composting and anaerobic digestion.
5. Innovative Technologies
Advancements in technology, such as smart packaging and sensors, can help monitor and reduce food waste at various stages of the supply chain. Additionally, utilizing food waste for bioenergy generation through anaerobic digestion can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion
Food waste is a global issue with far-reaching impacts on the environment, economy, and society. Addressing this problem requires a systemic approach involving individuals, businesses, governments, and organizations. By taking action to reduce food waste, we can alleviate hunger and poverty, conserve resources, mitigate climate change, and build a more sustainable and equitable world.